Diabetes, Foot and Footwear
Diabetes, Foot and Footwear:
Diabetes Mellitus is a Greek word meaning Siphon – to pass through and Mellitus a Latin word meaning sweet. Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease wherein the blood sugar levels are inappropriately elevated. There are several categories of DM, Including Type 1, Type 2, Gestational Diabetes, Maturity onset diabetes of the young (MODY), Neonatal Diabetes, Secondary diabetes because of some drug use…As Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disease characterized by elevated levels of blood glucose it leads over time to serious damages to heart, Kidney, eyes, blood vessels and nerves. Here we will look into how Diabetes affects the Foot.
A debilitating complication of diabetes mellitus is diabetic foot ulcers (DFU) which leads to increased overall morbidity in patients. However, this complication could be prevented by proper footcare and checking on the controllable factors that cause DFU.
The burden of Diabetes foot ulcer is alarmingly high and there are number of stats which prove the same.
- India being the Diabetes Capital of the World has a Prevalence of 65.1 million suffering from DM of the Entire Indian Population being 1.33 billion of Worlds 6 billion people.1
- Data reports that the lifetime risk of a person with diabetes having a foot ulcer is as high as 25 %. Also the most common reason accounting to approximately 30 % for hospitalization of patients with diabetes has been reported as diabetic foot ulcers.2
- It is also been noted that 10–15 % of patients suffering from Diabetic Foot Ulcer require expert management or multi disciplinary approach.1
- Rough estimates are at about 1,00,000 lower limbs are amputated (non traumatic) in India every year, of which at least seventy-five percent are neuropathic feet with secondary infections and are potentially preventable. 1
Management of diabetic foot disease requires multidisciplinary team approach and potentially can reduce the incidence of total amputation number by 49–85 % in the at-risk diabetic foot.
There are multiple factors that contribute to Diabetic foot Ulcers, the most prominent ones being Peripheral Neuropathy and Peripheral Vascular Disease
-
- Peripheral Neuropathy
- Peripheral Vascular Disease
- Foot Deformity (Bony Prominences) / Limited joint Mobility
- Previous Ulceration/Amputation
- Poor Controlled Diabetes / Duration of Diabetes
- High Plantar Pressure
- Inappropriate Footwear
- Barefoot walking
- Poor eyesight
- Unable to reach/care for feet
- Gender (Male), Age and High BMI
- Lack of Knowledge / Inappropriate Foot self-care practices
- Smoking
- Activity Level /Prolonged standing
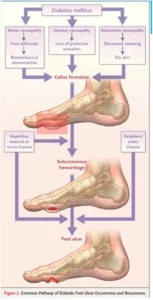
Its worthwhile to understand the common patway of occurrence and recurrence of DFU which is self explanatory. It was published in N Eng Journal of medicine by Prof Amstrong et al Diabetic foot ulcers can be classified in number of ways based of underlying pathophysiology
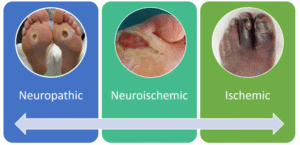
In Neuropathic ulcers
- Generally painless
- Planter weight – bearing area
- Moderate or high exudate
- Palpable Pulses –ABI > 0.8 Toe pressure >45 mmHG
- Insensate Foot
In Ischemic Ulcers
- Borders / dorsum of foot
- Minimal or no peri wound callous
- Painful
- Irregular edges
- Punched out appearance
- Necrotic
- Weak or Non –Palpable Pulse
- ABI < 0.8 Toe pressure <45 mmHG
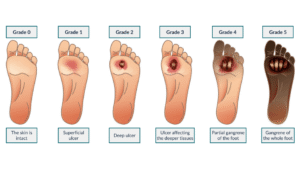
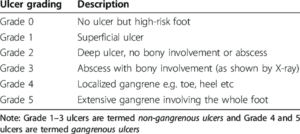
Based on wound depth and necrotic tissue, Diabetic ulcers can be classified by Wagner Ulcer Classification system.
Now we know the factors leading to DFU’s , In this we noted an important factor as foot deformity could be a risk factor for development of Diabetes foot Ulcers. Let’s look into the foot deformities that are predisposing to ulceration
- Clawed Toes/Hammer Toe
- Bunions
- Pes Cavus (High Arch)
- Pes Planus (Flat Feet)
- Nail Deformities
- Charcot foot
- Deformities from previous trauma or surgery
- Hallux Rigidus
- Hallux Varus/Hallux Valgus
- Ankle Equines …
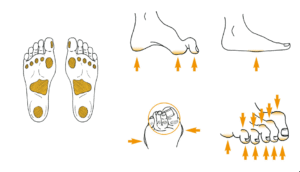
Understanding the foot deformities helps us to assess the area that are more prone for ulceration .Areas of the foot that are more prone for ulceration are Taken from .IWGDF Guidelines on the prevention and management of diabetic foot disease-Nicolaas C. Schaper1, Jaap J. van Netten2,3,4,Jan Apelqvist5, Sicco A. Bus2, Robert J. Hinchliffe6,Benjamin A. Lipsky7 on behalf of the International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot (IWGDF)
As you would agree once you know the risk factors the best strategy is to focus on prevention of ulceration. This is critical to avoid infection, hospitalization and even amputation. So, what’s that you need to do
- Patient education and awareness: Inspection of foot daily (using a mirror or help if needed). See for redness, swelling, Callus or wound and seek intervention. Patient needs to be aware walking barefoot increases the ulceration risk manifold even when walking indoors.
- Glycemic control: Maintain good blood sugar levels (target Hba1c < 7% ).
- Regular foot examination: Apart from self-examination clinical examination at least once in 6 months ( more frequently for high risk patients) check for peripheral neuropathy and ischemic changes.
- Skin and Nail Care: Wash feet daily and pat dry it esp between toes, Apply moisturizer to prevent dryness (but not between toes) ,Trim nails straight across to avoid ingrown nails.
- Footwear and Off loading: Wear properly fitting shoes with cushioned insoles (MCR/MCP footwear for high risk patients) preferably custom made orthotics, Avoid tight, pointed or high heeled shoes. It has to have wide toe box with depth. The footwear should be seamless to prevent aberrations. Patients with risk to have forefoot ulcers should avoid flip flops or footwear models with toe stick. For diabetic patients in general its advisable to have footwear with back counter(Back covered like in shoes) . If the patient has neuropathy the risk of ulceration is super high and so should preferably have a rocker bottom footwear with rigid outer sole. This helps distribution of pressure and reduces the risk of Charcot foot ulceration.
- Other risk factor management: Stop smoking, Regular exercise as per dr advise, have your BP and Cholesterol in control, Very important do not self-treat without having the expertise, do not try to remove callus and corns by yourself. Seek professional care.
Once a person develops a diabetic foot ulcer the patient needs an offloading device or footwear. The level of off loading depends on the severity of the ulcer and area of the ulcer. Remember at this stage the patient needs to know footwear is no longer a footwear and it is a therapeutic device.
IWGDF (International work group on Diabetic foot) guidelines best explains the different scenarios and corresponding therapeutic footwear and off loading to be done. I am attaching the same for your understanding
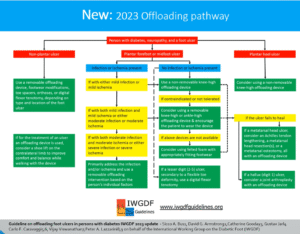
IWGDF has also given us the definition for therapeutic foot wear and off loading devices Custom-made (medical grade) footwear: Footwear uniquely manufactured for one person, when this person cannot be safely accommodated in conventional footwear. It is made to accommodate deformity and relieve pressure over at-risk sites on the plantar and dorsal surfaces of the foot.
In-depth assessment, multiple measurements, impressions or a mould, and a positive model of a person’s foot and ankle are generally required for manufacture. This footwear includes a custom-made insole.



Offloading device: any custom-made or prefabricated device designed with the intention of relieving mechanical stress (pressure) from a specific region of the foot (e.g. total contact cast (TCC), (non-)removable walker, knee-high walker, ankle-high walker, ankle foot orthoses, cast shoe, forefoot offloading shoe, Heel Offloading Shoes etc.).
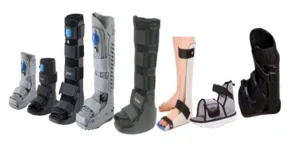
Air walker boots (Air casts),helps patients with diabetesby reducing pressure on the foot and ankle,which can help protect soft and bony tissues:
Immobilization
The boot limits the movement of the foot and ankle, which can help reduce friction and shear on the skin.
Healing
The rocker sole and pressure relieving insole can help offload pressure on the foot and eliminate pressure points
Offloading Pressure
The action of the air cells helps push edema out of the joint space,which can improve circulation and healing time.The air bladders can be adjusted to control swelling ,It reduces Micro trauma & is comfortable providing a well isolated protection zone for the foot & leg.
As per prof David.G.Amstrong in a patients with Diabetic foot ulcer Its not What you put on but What you take-off heals the wound

The central tenet of any treatment plan addressing neuropathic diabetic foot wounds is the appropriate debridement of nonviable tissue coupled with adequate pressure relief (off-loading). Although numerous advances have been made in the treatment of diabetic foot wounds, including bioengineered tissues, autologous and exogenous cytokine delivery systems, and potentially effective topical antimicrobial modalities, none will succeed without addressing effective debridement and off-loading.1
- It’s Not What You Put On, but What You Take Off: Techniques for Debriding and Off Loading the Diabetic Foot Wound -David G. Armstrong, Lawrence A. Lavery, Brent P. Nixon, Andrew J. M. Boulton – Clinical Infectious Diseases, Volume 39, Issue Supplement_2, Published: August 2004, Pages S92–S99,
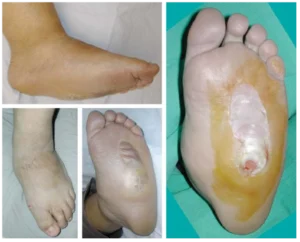
Once Charcot foot develops it requires special kind of footwear that accommodates the Charcot, giving ankle stability, Off Loading ,additionally reducing the loading in the foot with high Ankle orthosis ,Rocker bottom also reduces the loading in the foot with weight distribution.

Review published in the August 24 issue of Advances in Therapy. On the topic Progress Stalled in Diabetic Foot Ulcers; Major Unmet Need says
The best thing is to try to prevent diabetic foot ulcers from developing [in thefirst place] with patient education, appropriate footwear, and regular care,

